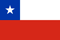
Types of worms and their classification
- Biological helminths - the eggs and larvae of this group of parasites mature in animal organisms (cattle, dogs, cats) or insects (mosquitoes, flies). that is, human infection occurs directly from them. And transmission from one person to another is impossible.
- Soil Worms – The eggs and larvae of this group of parasites mature only in the soil (i. e. outside the human body).
- Exposure to parasites – Infections are passed directly from sick to healthy people (via handshakes, household items, bedding, etc. ).
- Round parasites (nematodes) come in different sizes and appearances, and always have different sexes. These include pinworms and roundworms (pictured).
- Tapeworms, or flat (ribbon-shaped) worms, are long worms that feed through their own skin. These include the bovine and pork tapeworms (very common) and the Echinococcus tapeworm (pictured).
- Flukes or trematodes - Opiozoria, schistosomiasis and some other types of parasitic microorganisms.
Tapeworms and flukes are always parasites, but there are more than 10, 000 species of roundworms, only some of which can live in the human body.
Brief characteristics of common parasites
- Ascariasis (Ascariasis).
- Toxocariasis (Toxocariasis).
- Whipworm (trichocephalosis).
- Trichinosis (trichinellosis).
- Tapeworm or cattle tapeworm (taeniarinhoz).
- Pork tapeworm (diseases - taeniasis, cysticercosis).
It is important to note that treatment also depends on the type of parasitic microorganism, the intensity of the worm infestation and the number of worms that have invaded the body.
Roundworm, Toxocara
- General malaise and weakness.
- Tension increases.
- Increased body temperature.
- Shortness of breath, dry cough.
- Pain in the sternum area.
- Allergic reaction, manifested by rash, itching, and redness of the skin.
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
- A dry cough develops.
- Dry wheezing when breathing.
Whipworm, Trichinella spiralis
- Pale skin.
- Weakness, nausea.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Abdominal pain syndrome.
- There is blood mixed in the stool.
- Increased irritability and convulsions.
- Headache, dizziness.
- There is pain in the abdomen.
- Often nauseated.
- Vomiting, damage to the digestive tract.
- Loss of appetite.
Treatment includes anthelmintics as well as symptomatic treatment to combat allergy symptoms. When the temperature is high, it is recommended to take antipyretic drugs. Typically, treatment takes place in a hospital setting.
Beef and pork tapeworms
- Systemic abdominal pain.
- nausea.
- Loss of appetite and vomiting.
- Weight loss.
- Increased gas formation.
- Requires up to 5 bowel movements per day.
- Cysticercosis, when larvae enter the body.
- Taeniasis - adults "live" in the body.
- Anaphylaxis, shortness of breath.
- Abdominal pain and difficulty in defecation.
- Loss of appetite and gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Sleep disturbance, nervousness, excitement.